Coronary heart disease, also known as coronary artery disease, is the most common type of heart disease. It is the number one cause of death for adults in the United States. For some, it may also be preventable. Richmond University Medical Center provides top-notch cardiovascular services and other medical care on Staten Island. Here, we outline what coronary heart disease is and some ways to help prevent it.
What Is Coronary Heart Disease?
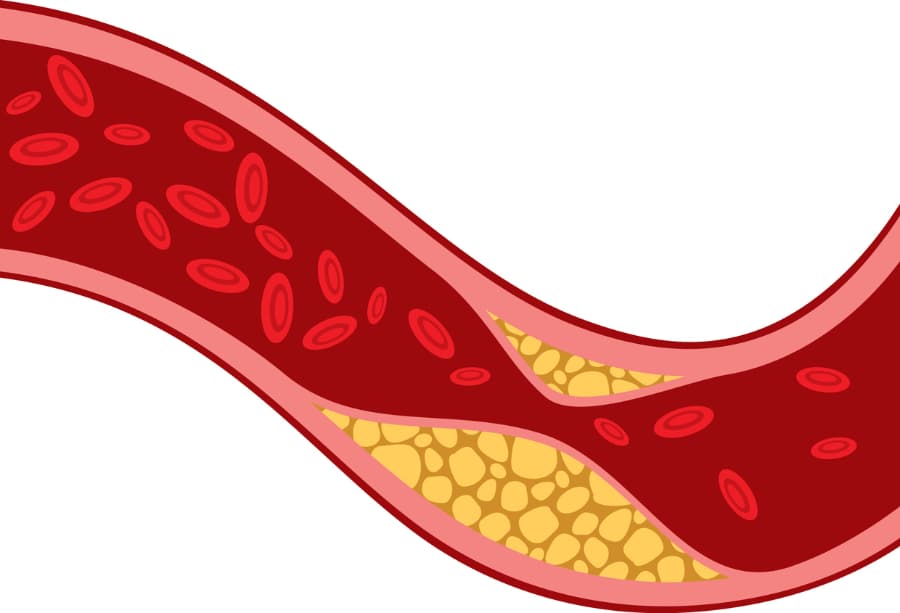
Heart disease causes the arteries—vessels that bring blood to the heart—to thicken and narrow. This thickening prevents oxygen and nutrients from getting to the heart. The lack of blood can lead to chest pain. Over time, the heart needs to work harder, which can lead to heart failure. You may also develop an irregular heartbeat or arrhythmia. If the artery walls become too thick, you may have a heart attack.
Symptoms of Heart Disease
There are a number of signs of heart disease you should watch out for:
- Vomiting, nausea, or indigestion
- Pain, numbness, weakness, or coldness in your arms and legs
- Pain, tightness, and pressure in the chest
- Shortness of breath
- Pain in the jaw, neck, upper abdomen, or back
If your pain gets worse or you feel unwell, go to the emergency department right away. At Richmond University Medical Center, our emergency cardiac care center has state-of-the-art equipment and innovative medications to help us treat heart attacks and blood clots.
Risk Factors of Heart Disease
Coronary heart disease forms over a patient’s lifetime. Certain risk factors and habits can increase your chance of developing it:
- Not exercising enough
- Poor diet
- Chronic stress and fatigue
- Excessive drug and alcohol use
- Smoking
- Depression
If you have any of these risk factors, talk to your primary care provider on Staten Island.
How to Decrease Your Risk
The best way to prevent coronary artery disease is by controlling your risk factors, including:
Quitting Smoking
Smoking is one of the biggest causes of heart disease and heart attacks. Secondhand smoke is also dangerous. By quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke, you can reduce your risk.
Eating Less Unhealthy Foods
Foods high in saturated fats, trans fats, salt, and sugar can cause plaque to form. As plaque builds up, your arteries start to narrow. Plaque can also break off from your coronary artery wall and form a clot, which can cause a heart attack.
Foods high in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fat such as olive oil and fish can help prevent this buildup. Plant fiber is a heart-healthy food that also aids digestion.
Getting Enough Exercise
Exercise is one of the best ways to reduce your risk of coronary heart disease. You should aim to be active for at least 30 minutes a day. Another good goal is to get at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. If you are a runner, aim for 75 minutes of aerobic exercise weekly.
Maintaining a Healthy Body Weight
Being obese and overweight can put extra, unwanted stress on your heart. Losing just five to 10% of your current weight can lower your risk of developing coronary heart disease or a heart attack.
Finding Healthy Stress Outlets
While having some stress is unavoidable, having too much can lead to heart disease. Excess stress can cause you to overeat, drink, or sit for long periods. Finding ways to offload some of the extra stress in a relaxing and healthy way can reduce your risk.
Some heart-healthy ways to manage stress include:
- Meditation
- Relaxing with friends
- Kickboxing
- Stress-management programs
- Yoga
- Coloring or a similar creative outlet
Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease
Due to it developing over time, the first sign of coronary artery disease may be shortness of breath or chest pains with physical exertion. However, sometimes the first sign is more serious like a heart attack.
Your physician will look at markers such as blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood glucose to diagnose coronary artery disease. They may also take a family history. Depending on your symptoms, they may also administer any number of tests to gain additional information:
- Coronary calcium testing: A CT scan that shows images of the calcium and plaque buildup in your heart
- Electrocardiograms (EKG or ECG): Measurement of your heart’s electrical activity while you are resting
- Exercise stress test: A test that measures your heart rate while on a treadmill
- Echocardiogram: A test allowing your physician to view your heart under ultrasound
- Cardiac catheterization: A test where a thin tube is placed into your artery to check for blockages
Receive Cardiovascular Treatment on Staten Island, NY
At Richmond University Medical Center, our mission is to inform patients and provide top-notch healthcare services to the communities of Staten Island, New York. Our board-certified physicians have won national awards for exceptional cardiovascular care. If you are concerned about your heart or have been recently diagnosed with coronary artery disease, contact us today to schedule an appointment.